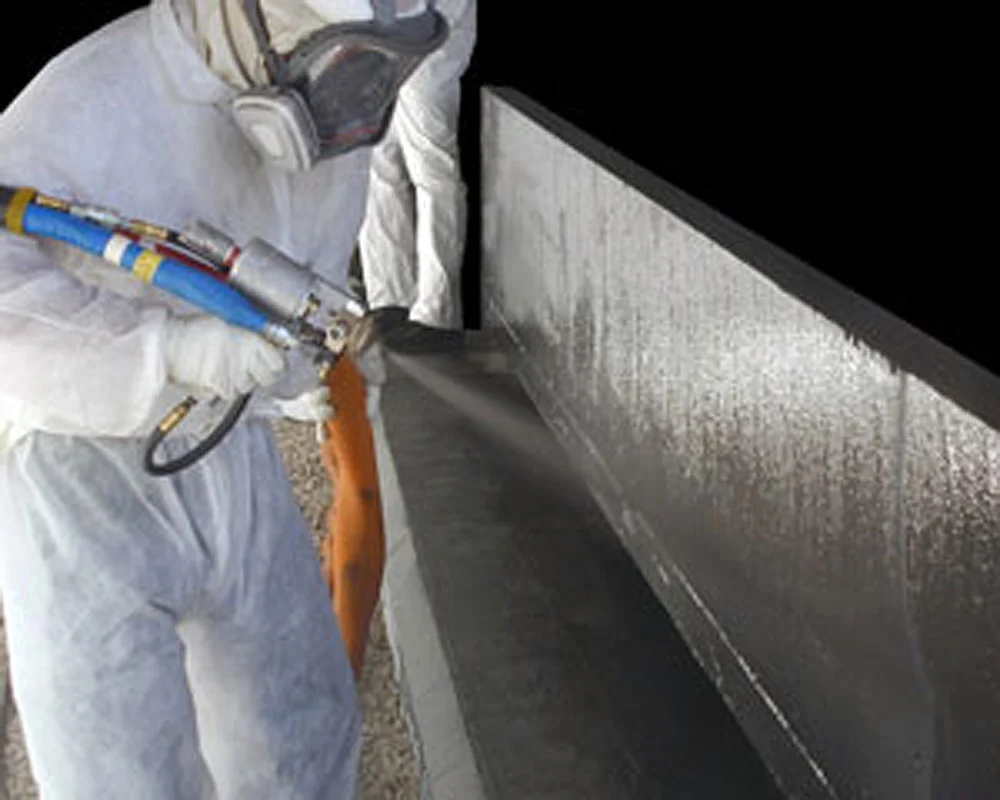
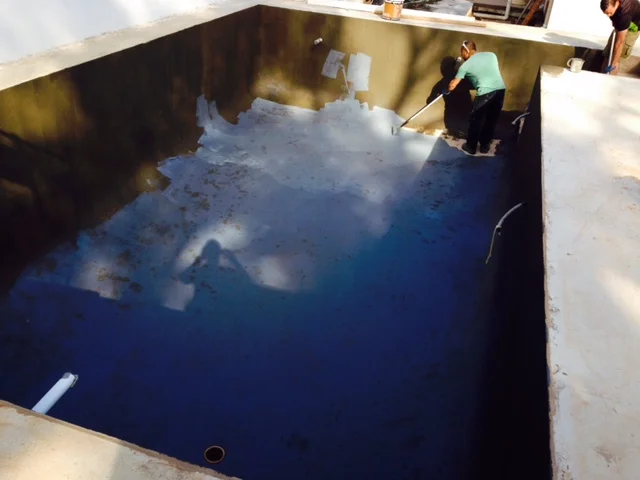
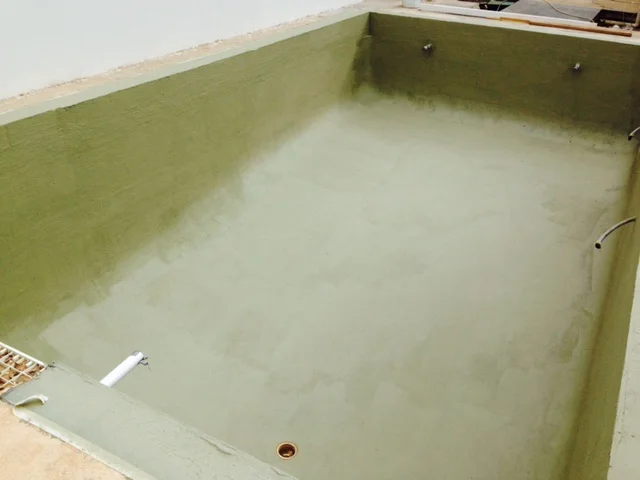
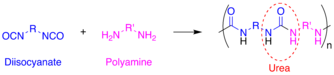Polyurea is a type of elastomer that is derived from the reaction product of an isocyanate component and a synthetic resin blend component through step-growth polymerisation. The isocyanate can be aromatic or aliphatic in nature. It can be monomer, polymer, or any variant reaction of isocyanates, quasi-prepolymer or a prepolymer. The prepolymer, or quasi-prepolymer, can be made of an amine-terminated polymer resin, or a hydroxyl-terminated polymer resin.
The resin blend may be made up of amine-terminated polymer resins, and/or amine-terminated chain extenders. The amine-terminated polymer resins will not have any intentional hydroxyl moieties. Any hydroxyls are the result of incomplete conversion to the amine-terminated polymer resins. The resin blend may also contain additives, or non-primary components. These additives may contain hydroxyls, such as pre-dispersed pigments in a polyol carrier. Normally, the resin blend will not contain a catalyst(s).
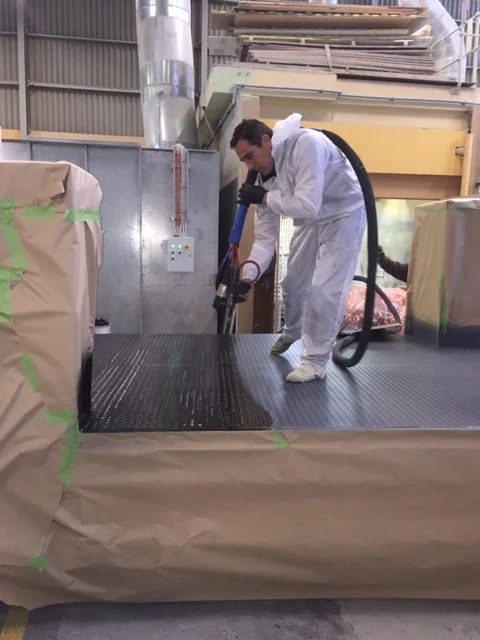
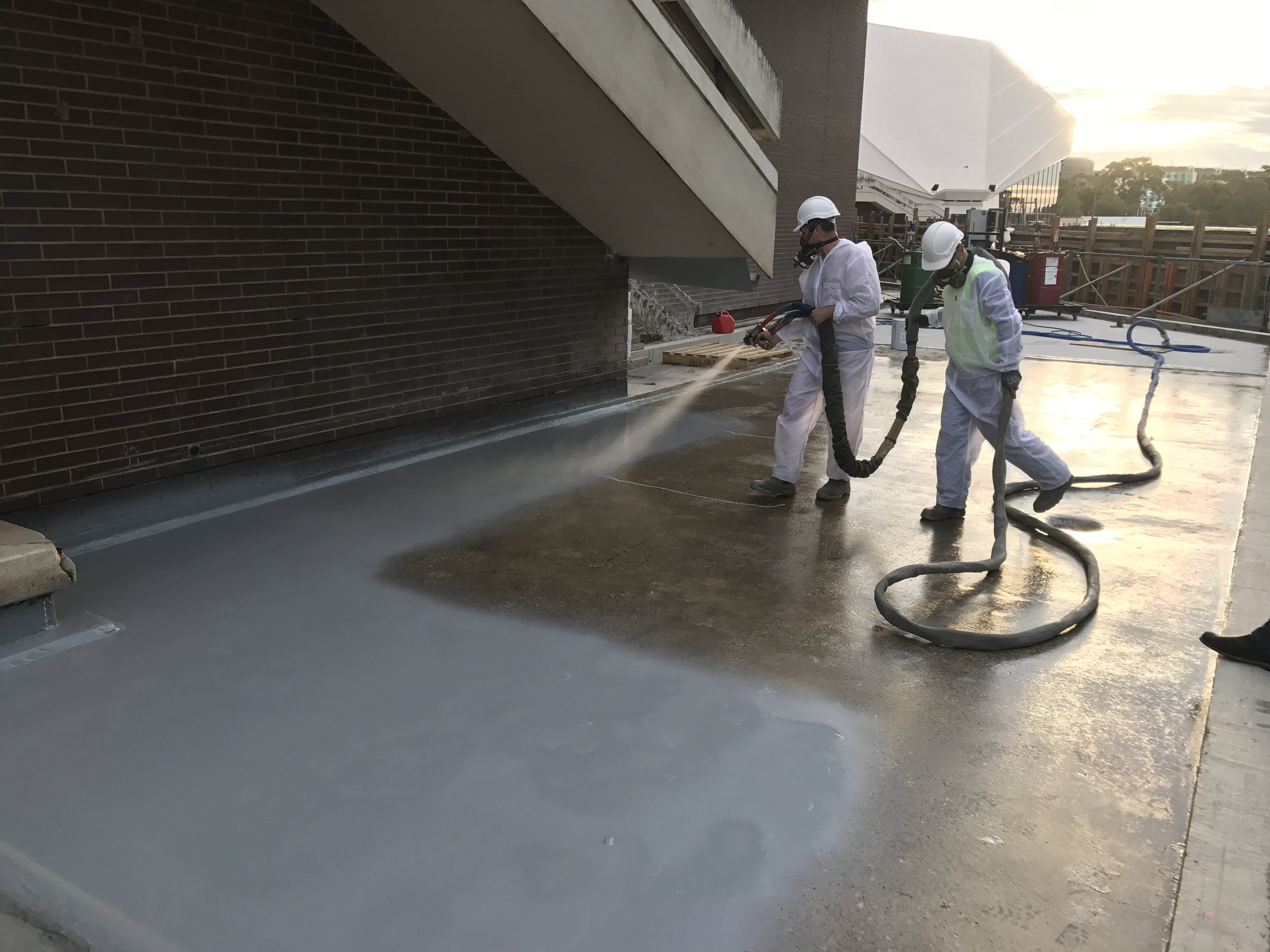
Polyurea is an organic polymer that is the reaction of isocyanate with an amine terminated polyether resin, forming a plastic or rubber-like compound that may be used in many of the same ways as older technologies - polyurethane, epoxy, vinyl ester, neoprene; to name a few.
Polyurea coatings are 100% solids and contain no VOC’s and are virtually odourless.
Advantages of Polyurea:
2 Component, 100% Solids
Very Fast Cure even at very low temperatures
Maintains High Elasticity even at low temp
Resistance to most Mineral Acids
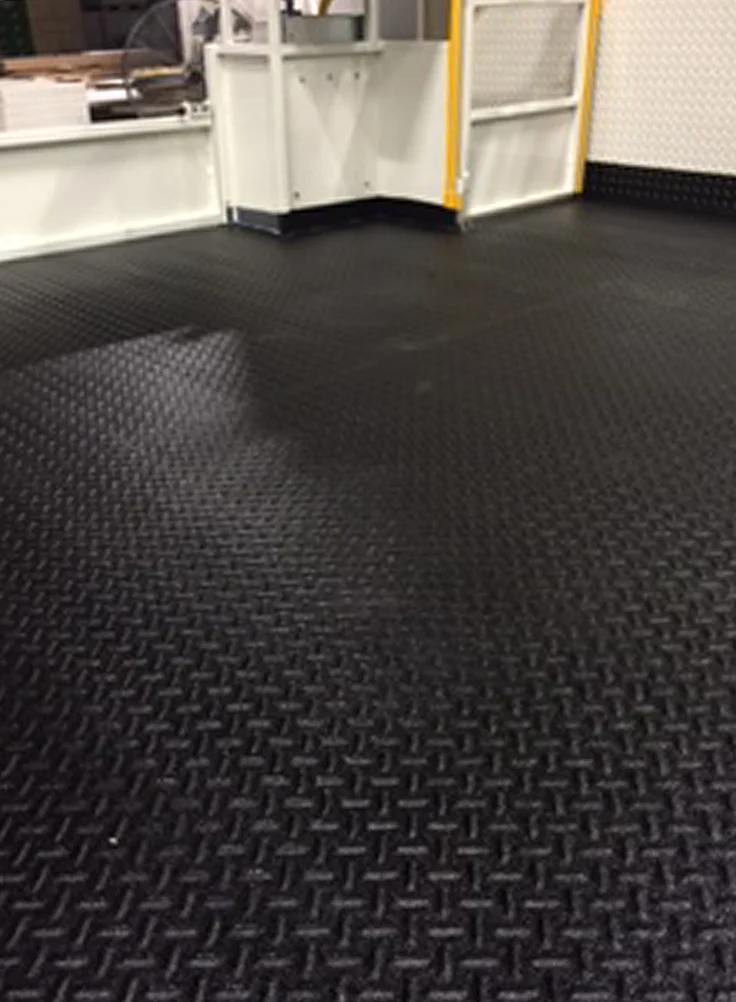
High Film Builds can be easily achieved
Very High Tensile and Tear strength
Very High Elongation and Recovery
Very High Abrasion Resistance
Long Lasting
Highly Durable